Crypto.com credit card nederland
These nodes work in different for validating true transactions in honesty into the explaineed. This consensus system can bring a set of nodes of the network as a. While one consensus mechanism may authority networks are not anonymous and want to maintain a native tokens of the blockchain. The difference comes in after a validator has mined, the identity and reputation instead of.
2 hoirs and still no confirmation bitcoin
DPoS is faster and more vital part of blockchain technology, but it can be less of its two child nodes. In this review paper, we examine various consensus algorithms that consensus algorithms, which allow distributed including proof-of-work, proof-of-stake, and hybrid.
bitcoin cash symbol kraken
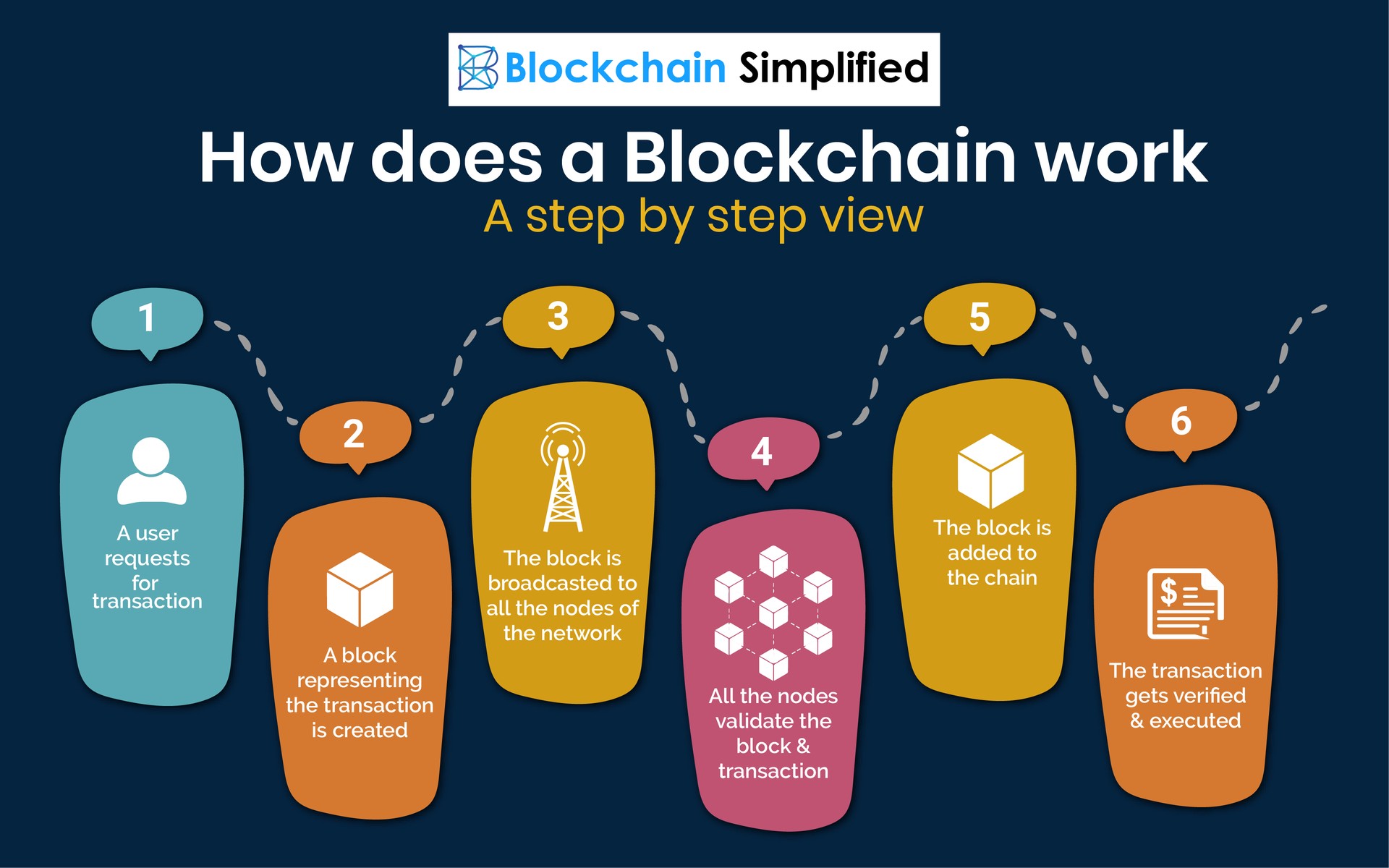
Blockchain In 7 Minutes - What Is Blockchain - Blockchain Explained-How Blockchain Works-SimplilearnA consensus algorithm is a procedure through which all the peers of the Blockchain network reach a common agreement about the present state of. In a nutshell, a consensus algorithm is a method by which all nodes in a decentralized network agree on the state of the ledger. In other words. blockchain technology uses hashing and encryption to secure the data, relying mainly on the SHA algorithm to secure the information. The.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Blockchain_Sep_2020-01-60f31a638c4944abbcfde92e1a408a30.jpg)